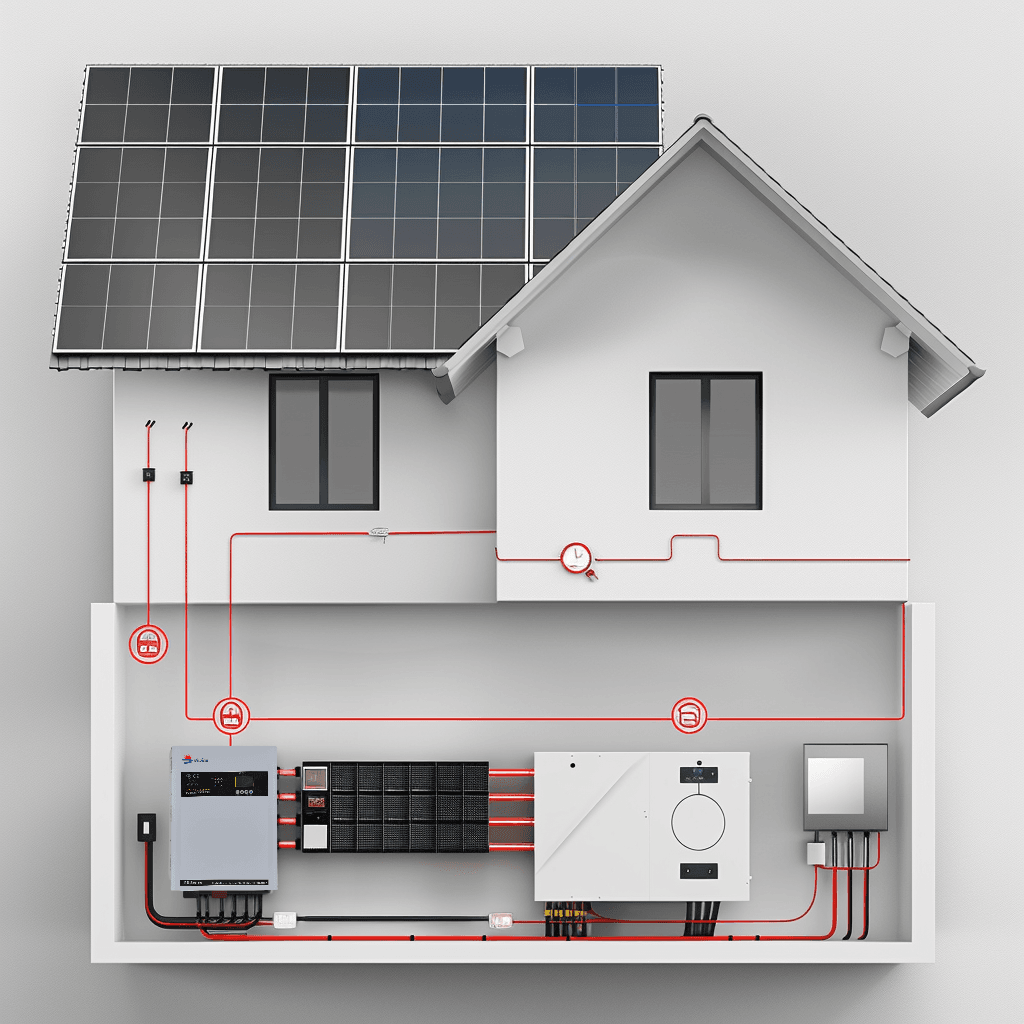
Small vs. Large Solar Systems: Key Differences
1. Small and Medium-Sized Solar Systems
- Applications: Primarily used in residential homes, small businesses, and community projects.
- System Size: Typically ranges from 1 kW to 100 kW.
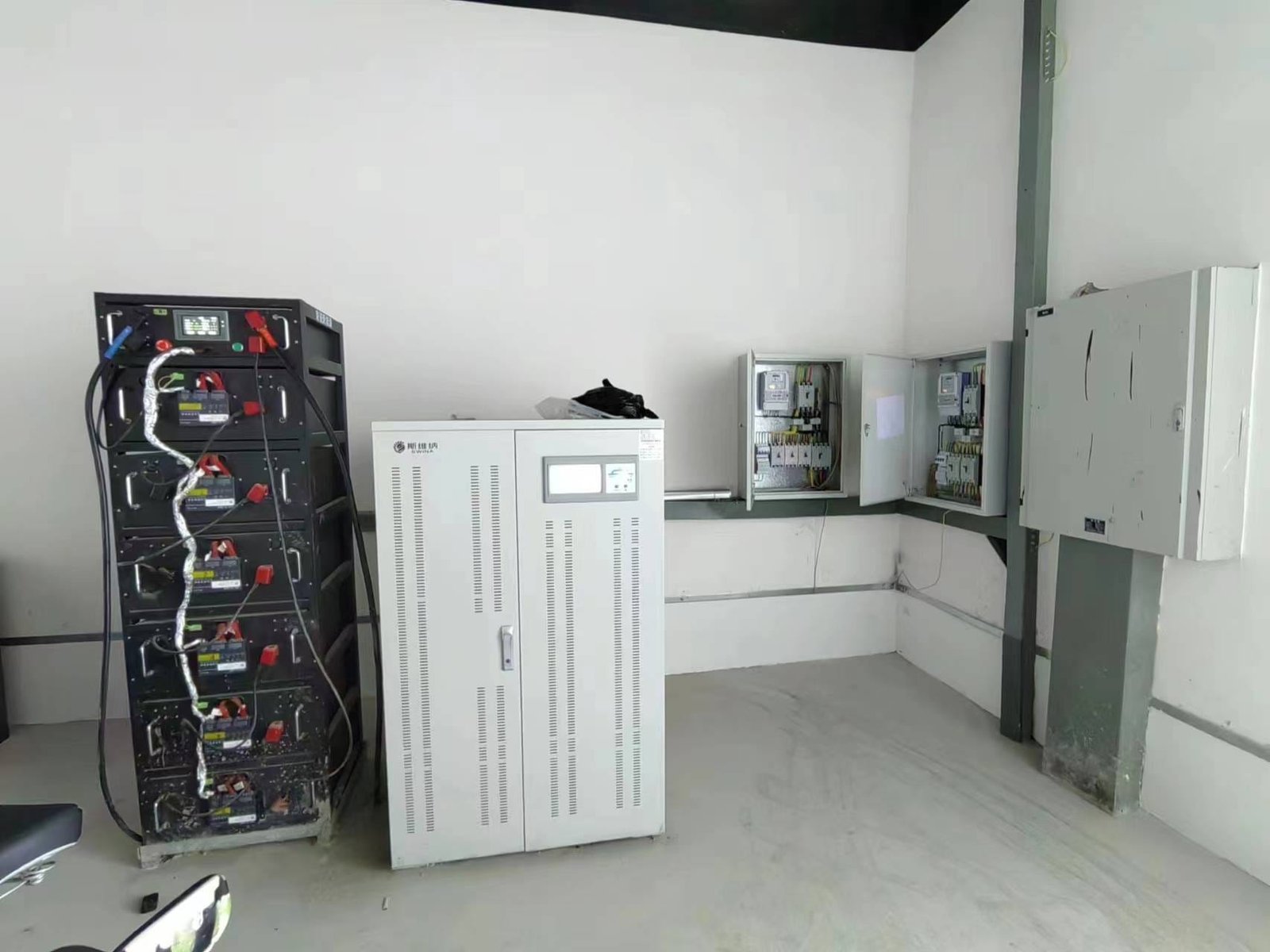
- Components: Includes solar panels, inverters, mounting systems, and sometimes battery storage.
- Installation: Relatively simple, often completed in a few days.
- Cost: Lower upfront investment, with prices ranging from 2,000to50,000 depending on size and location.
- Energy Output: Designed to meet the energy needs of a single household or small business.

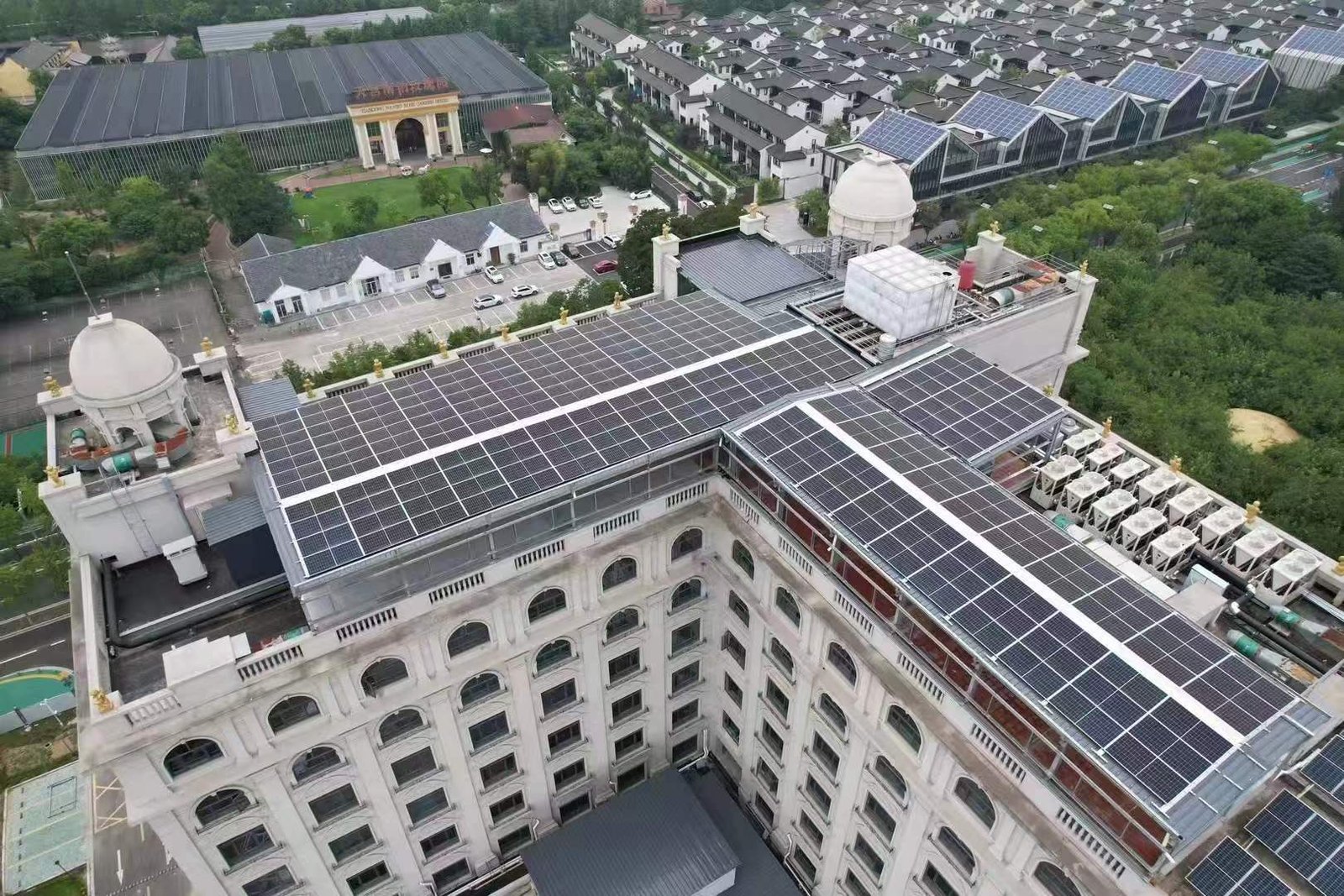
100kw three pahse inverter case(1) 
an off-grid inverter
Advantages:
- Affordability: Lower initial costs and shorter payback periods.
- Scalability: Easy to expand as energy needs grow.
- Incentives: Many governments offer subsidies, tax credits, and net metering for small-scale systems.
Challenges:
- Limited Energy Output: This may not meet the needs of high-energy consumers.
- Space Constraints: Requires adequate roof or ground space.
- Key Players: swina, Deye , Huanwei
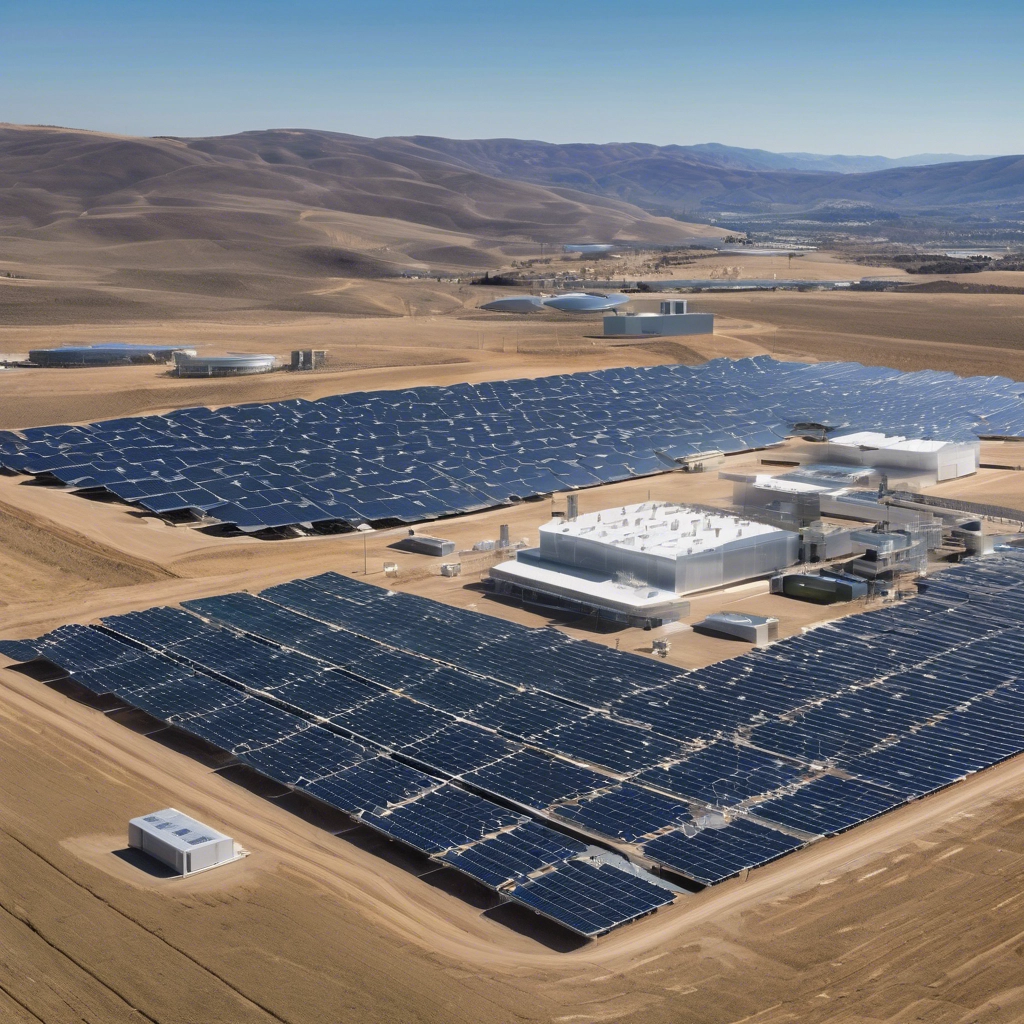
2. Large and Complex Solar Systems
- Applications: Used in industrial facilities, large commercial buildings, utility-scale solar farms, and government projects.
- System Size: Typically ranges from 100 kW to several megawatts (MW).
- Components: Includes high-capacity solar panels, advanced inverters, tracking systems, and large-scale battery storage.
- Installation: Complex, often requiring months of planning and construction.
- Cost: Higher upfront investment, ranging from $100,000 to millions of dollars.
- Energy Output: Designed to power large facilities or feed electricity into the grid.

solar power storage for a big project
Advantages:
- High Energy Output: Can meet the demands of energy-intensive operations.
- Economies of Scale: Lower cost per watt compared to small systems.
- Revenue Opportunities: Excess energy can be sold to the grid or used for power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Requires significant capital investment.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Complex permitting and compliance processes.
- Maintenance: Requires specialized expertise and regular upkeep.
Global Market Distribution
1. North America
- Market Overview: The U.S. and Canada are leaders in both residential and utility-scale solar installations.
- Trends:
- Rapid growth in residential solar due to falling costs and federal tax credits.
- Utility-scale projects dominate the market, driven by corporate PPAs and renewable energy mandates.
- Key Players: Tesla, SunPower, First Solar.
2. Europe
- Market Overview: Germany, Spain, and the UK are at the forefront of solar adoption.
- Trends:
- Strong government support through feed-in tariffs and subsidies.
- Increasing focus on energy storage and hybrid systems.
- Key Players: SMA, Fronius, Enphase.
3. Asia-Pacific
- Market Overview: China, India, and Japan are the largest markets in the region.
- Trends:
- China leads in both manufacturing and installation of solar systems.
- India is rapidly expanding its solar capacity to meet growing energy demand.
- Japan focuses on residential solar and energy self-sufficiency.
- Key Players: Sungrow, Huawei, Tata Power.
4. Middle East and Africa
- Market Overview: Solar adoption is growing, driven by abundant sunlight and energy access initiatives.
- Trends:
- Large-scale solar farms are being developed in countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
- Off-grid solar systems are gaining traction in rural areas.
- Key Players: ACWA Power, Scatec Solar.
5. Latin America
- Market Overview: Brazil, Mexico, and Chile are leading the solar market in the region.
- Trends:
- Favorable policies and auctions for utility-scale projects.
- Increasing adoption of residential solar systems.
- Key Players: Enel Green Power, Canadian Solar.
Market Trends and Commercial Opportunities
1. Falling Costs
- The cost of solar panels and installation has dropped significantly over the past decade, making solar energy more accessible to both residential and commercial users.
2. Energy Storage Integration
- The integration of battery storage systems is becoming increasingly popular, allowing users to store excess energy for use during peak hours or power outages.
3. Corporate Renewable Energy Adoption
- Many corporations are investing in large-scale solar projects to meet sustainability goals and reduce energy costs.
4. Government Policies and Incentives
- Governments worldwide are offering incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and net metering to promote solar adoption.
5. Technological Advancements
- Innovations in solar panel efficiency, smart inverters, and tracking systems are driving the growth of the solar industry.
6. Emerging Markets
- Developing countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America present significant growth opportunities due to rising energy demand and government support.
Future Outlook
The solar energy industry is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, falling costs, and increasing environmental awareness. Key trends to watch include:
- Hybrid Systems: Combining solar with wind or other renewable energy sources.
- Floating Solar Farms: Utilizing water bodies for solar installations.
- AI and IoT Integration: Smart energy management systems for optimized performance.
The solar energy industry offers immense opportunities for businesses, investors, and consumers alike. Whether you’re considering a small residential system or a large commercial installation, understanding the market dynamics and trends is key to making informed decisions. By staying ahead of the curve, you can capitalize on the growing demand for clean, renewable energy and contribute to a sustainable future.
Ready to explore solar energy solutions for your home or business? Contact our team of experts today for a personalized consultation!