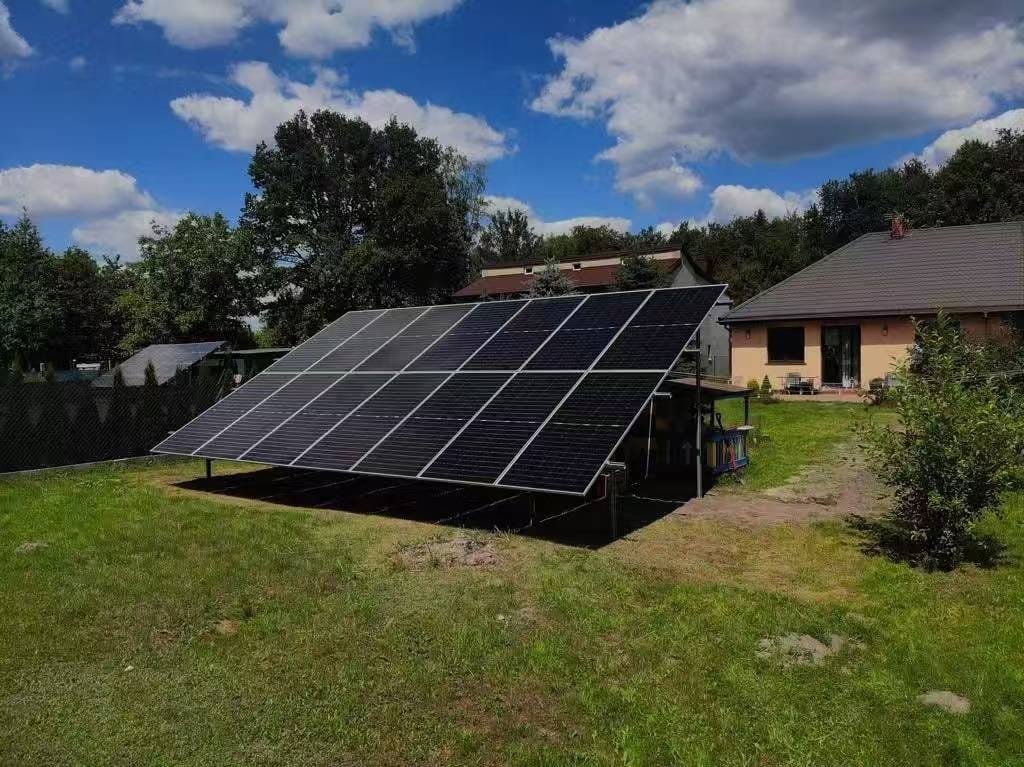
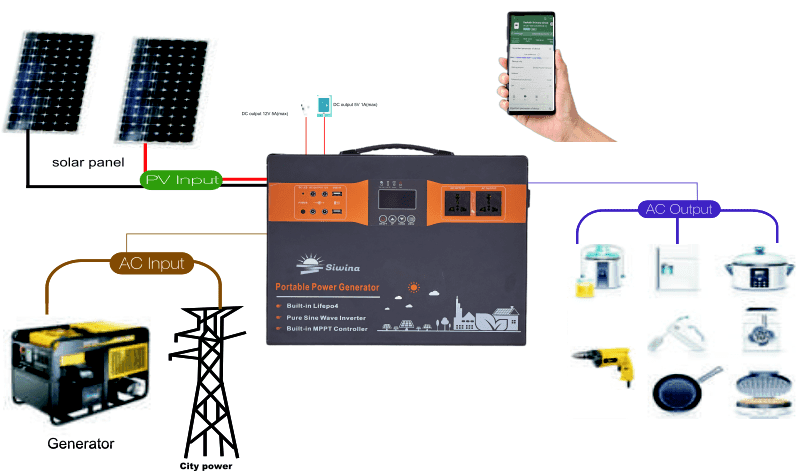
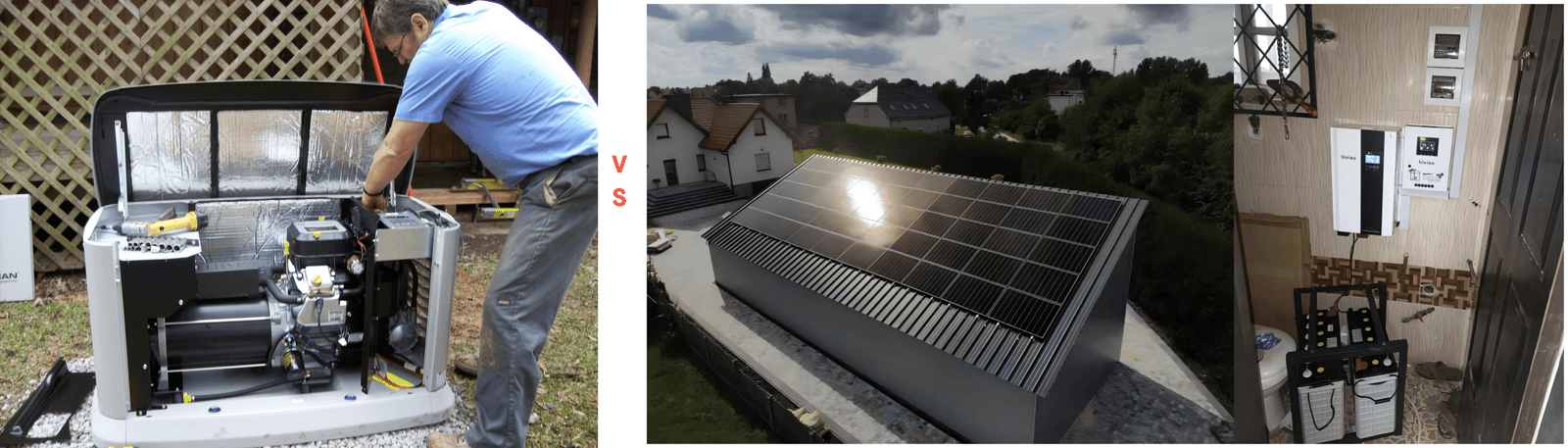
What is an Off-Grid Solar Inverter?
An off-grid solar inverter is the core component of an off-grid solar system. It converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use by household appliances and equipment. Unlike grid-tied inverters, off-grid inverters do not rely on the grid. Instead, they work in conjunction with battery systems to ensure continuous power supply in areas without grid access or where the grid is unstable.

Key Differences Between Off-Grid and Grid-Tied Inverters (Comparison Table)
| Aspect | Off-Grid Solar Inverter | Grid-Tied Solar Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Dependency | Fully independent, no grid connection required | Must be connected to the grid to operate |
| Core Function | DC→AC conversion + battery management + load control | Only DC→AC conversion |
| Typical Applications | Remote areas, mobile devices, backup power | Standard residential grid-tied systems |
| System Complexity | Requires battery and charge controller | Direct connection to the grid |
| Cost Structure | Inverter + battery + controller (higher upfront cost) | Only inverter (long-term grid dependency) |
📌 Engineer’s Insight: Off-grid systems are 3-5 times more complex than grid-tied systems. The inverter must act as both a “power dispatcher” and a “battery manager.”
A Step-by-Step Guide for Homeowners and Installers:https://swninverter.com/how-to-install-a-solar-power-system-a-step-by-step-guide-for-homeowners-and-installers/
Features of a High-Quality Off-Grid Solar Inverter
1. High-Efficiency Energy Conversion
- Function: Converts DC power from solar panels into AC power with an efficiency rate typically above 90%.
- Importance: Higher efficiency means less energy loss and better overall system performance.
2. Battery Management
- Function: Built-in charge controller to intelligently manage battery charging and discharging, extending battery life.
- Importance: Prevents overcharging or deep discharging, ensuring system stability.
3. Multi-Mode Operation
- Function: Supports solar priority, grid priority, or hybrid modes to adapt to different energy needs.
- Importance: Enhances system adaptability and reliability.
- Example: Seamless switching between solar, grid, and generator power in less than 10ms ensures uninterrupted power for critical devices like computers in offices or supermarkets.
4. Smart Monitoring
- Function: Real-time monitoring of system status (power generation, battery status, and load conditions) via LCD screens or mobile apps.
- Importance: Allows users to track system performance and troubleshoot issues promptly.

1kw 5kw all-in-one solar generator
5. High Load Capacity
- Function: Capable of powering multiple household appliances simultaneously, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and TVs.
- Importance: Meets diverse energy needs.
6. Non-Linear Load Compatibility
- Challenge: Handles instantaneous surge currents from inductive loads like air conditioner compressors.
- Performance Standards:
- Peak power ≥ 3 times rated power (e.g., a 5kW inverter should support 15kW surge loads).
- Waveform distortion rate < 3% (ensures safety for sensitive equipment).
7. Durability and Reliability
- Function: Built with high-quality materials and advanced technology to ensure stable operation in harsh environments.
- Importance: Reduces maintenance costs and extends equipment lifespan.
Three Economic Models for Off-Grid Systems (For Importers)
▶ Model 1: Diesel Replacement
- Typical Scenario: Island communication base stations.
- Economic Comparison:
- Diesel power cost: $0.45/kWh.
- Off-grid solar cost: $0.18/kWh.
- ROI: Payback in 3.2 years (system lifespan: 15 years).

diesel power generator vs solar power generator min
▶ Model 2: Grid Extension Cost
- Typical Scenario: Remote village electrification.
- Cost Comparison:
- Grid extension cost: $15,000/km.
- Off-grid system cost: $8,000/household (including 5kWh storage).
- Social Value: World Bank data shows that off-grid solutions have increased electrification rates in Africa by 37%.
▶ Model 3: Emergency Power Premium
- Typical Scenario: Data center backup power.
- Value Proposition:
- Cost of power outage: $9,000/minute (financial industry).
- Off-grid system switching time: 8ms (outperforms diesel generators’ 30s).
- Premium Pricing: Customers are willing to pay 3 times the price of conventional products.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar Inverters
- Energy Independence: No reliance on the grid, ideal for remote or unstable grid areas.
- Eco-Friendly: Reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions.
- Cost-Effective: Significantly reduces electricity bills, especially in areas with high grid connection costs.
- High Reliability: Ensures continuous power supply during grid failures or outages.
- Scalability: Easily expandable by adding more solar panels or batteries.
Applications of Off-Grid Solar Inverters
- Remote Area Electrification: Provides stable power to rural, mountainous, or island regions.
- Home Backup Power: Supplies backup power during grid instability or outages.
- Commercial and Industrial Use: Reliable power solutions for factories, farms, and communication base stations.
- Mobile Power: Powers RVs, boats, and other mobile devices.
- Emergency Relief: Provides power for rescue equipment and temporary shelters during natural disasters.

off grid inverter use for everywhere min
How to Choose a High-Quality Off-Grid Solar Inverter?
- Determine Power Requirements: Choose an inverter with sufficient power to meet peak load demands.
- Check Battery Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with battery types (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion).
- Focus on Brand and Warranty: Choose reputable brands like Deye, Swina, SWN, or Growatt for quality and after-sales support.
- Consider Scalability: Select inverters that support the future expansion of solar panels or batteries.
- Review User Feedback: Learn from other users’ experiences to understand real-world performance.
- Verify Core Parameters:
- Test 100% load surge and drop (sustain for 1 hour).
- Trace key components (use internationally renowned brands).
- Inspect production processes (aging tests are essential).
- Certifications: Ensure compliance with CE, ROHS, and ISO 9001 standards.

Harnessing the full potential of solar energy: the 120a 150a 96v 100a swina mppt solar controller
Conclusion
Off-grid solar inverters are the heart of independent energy systems, offering efficiency, reliability, and flexibility. By understanding their features, advantages, and applications, importers, distributors, and users can make informed decisions to meet diverse energy needs. As technology advances, off-grid solar inverters will play an increasingly vital role in the future.
If you have further questions or need professional advice, feel free to contact our team for top-notch service and support!
Call to Action:
✅ Download the “Off-Grid Inverter Selection Guide” (includes 50+ brand comparisons).
✅ Schedule a product audit with our expert engineering team.
✅ Get the 2023 Off-Grid Market Regional Analysis Report.
[Success Story] An East African importer reduced customer complaints by 82% and increased annual profits by 270% through optimized inverter selection—your transformation opportunity starts now!